
elixir guitar strings
Picture of Guitar String for sale

Picture about

cheap guitar strings
Classical guitar Strings

picture about guitar string with key
See also: Classical guitar strings
Modern guitar strings are constructed of metal, polymers, or animal or plant product materials.

different color classical guitar strings
Instruments utilising "steel" strings may have strings made of alloys incorporating steel, nickel or phosphor bronze. Classical and flamenco instruments historically used gut strings, but these have been superseded by polymer materials, such as nylon and fluorocarbon materials. Bass strings for both instruments are wound rather than monofilament.Body (acoustic guitar)
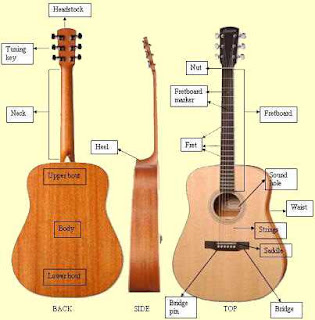
elements of Acoustic guitar
Body of Acoustic Guitar
See also: Sound boxIn acoustic guitars, string vibration is transmitted through the bridge and saddle to the body via sound board. The sound board is typically made of tone woods such as spruce or cedar. Timbers for tone woods are chosen for both strength and ability to transfer mechanical energy from the strings to the air within the guitar body. Sound is further shaped by the characteristics of the guitar body's resonant cavity.
In electric guitars, transducers known as pickups convert string vibration to an electric signal, which in turn is amplified and fed to speakers, which vibrate the air to produce the sounds we hear. Nevertheless, the body of the electric guitar still performs a role in shaping the resultant tonal signature.
In an acoustic instrument, the body of the guitar is a major determinant of the overall sound quality. The guitar top, or soundboard, is a finely crafted and engineered element made of tonewoods such as spruce and red cedar. This thin piece of wood, often only 2 or 3 mm thick, is strengthened by differing types of internal bracing. The top is considered by many luthiers to be the dominant factor in determining the sound quality. The majority of the instrument's sound is heard through the vibration of the guitar top as the energy of the vibrating strings is transferred to it.
Body size, shape and style has changed over time. 19th century guitars, now known as salon guitars, were smaller than modern instruments. Differing patterns of internal bracing have been used over time by luthiers. Torres, Hauser, Ramirez, Fleta, and C.F. Martin were among the most influential designers of their time. Bracing not only strengthens the top against potential collapse due to the stress exerted by the tensioned strings, but also affects the resonance characteristics of the top. The back and sides are made out of a variety of timbers such as mahogany, Indian rosewood and highly regarded Brazilian rosewood (Dalbergia nigra). Each one is primarily chosen for their aesthetic effect and can be decorated with inlays and purfling.
The body of an acoustic guitar has a sound hole through which sound is projected. The sound hole is usually a round hole in the top of the guitar under the strings. Air inside the body vibrates as the guitar top and body is vibrated by the strings, and the response of the air cavity at different frequencies is characterised, like the rest of the guitar body, by a number of resonance modes at which it responds more strongly.
Instruments with larger areas for the guitar top were introduced by Martin in an attempt to create louder volume levels. The popularity of the larger "dreadnought" body size amongst acoustic performers is related to the greater sound volume produced.
0 comments:
Post a Comment